Professor Zhou Yongsheng’s Research Team Developed a Programmed Drugs Delivery System for Efficient Bone Tissue Regeneration
On February 28, 2022, professor Zhou Yongsheng’s team published a research article on Chemical Engineering Journal (a top journal in Chemical Engineering) entitled “Programmed biomolecule delivery orchestrate bone tissue regeneration via MSC recruitment and epigenetic modulation”. Prof. Zhou Yongsheng and Prof. Lv Longwei from the Department of Prosthodontics are the corresponding authors of this paper. Dr. Wan Zhuqing, a post-doc from the Department of Prosthodontics is the first author of this work. This study is supported by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation and the Young Elite Scientist Sponsorship Program by CAST.
In last ten years, Prof. Zhou’s group has been reported the new application of several classical small molecular drugs for bone tissue engineering. The controllable release of these drugs to meet the changing demands during the process of bone defect healing is appealing but still challenging. In this study, a programmed delivery system was successfully fabricated via incorporating the near-infrared (NIR) light-responsive polydopamine-coated hydroxylapatite nanoparticles (nHA@PDA) into the thermo-responsive hydroxybutyl chitosan (HBC) hydrogel to regulate the therapeutic concentrations and timeframe of chemotactic simvastatin (SIM) and osteogenic pargyline (PGL). This designed smart hydrogel composite could perform an initial rapid release of SIM to meet the need of endogenous stem cell recruitment at the beginning of bone healing. Meanwhile, a flexible and NIR light-triggered increased release of PGL could promote osteogenic differentiation of migrated cells via a safe and stable epigenetic mechanism. Taken together, this on-demand delivery system successfully orchestrated the bone tissue regeneration, providing novel insights into the design of efficient delivery systems for bone tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
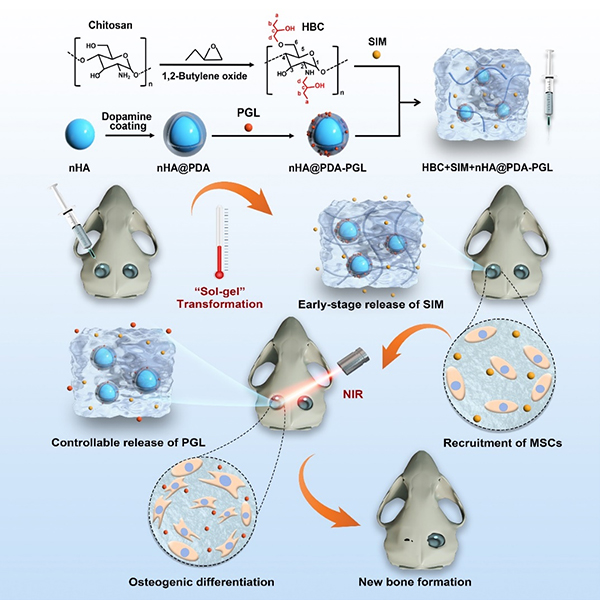
Fig. Schematic illustration of the programmed delivery system with on-demand release of small molecular drugs to orchestrate the processes in bone healing.
Online linkage: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135518